The ocean plays a crucial and irreplaceable role in the survival and development of human society. It is not only the cradle of life, but also a key component of the Earth's ecosystem. In order to protect this vast and boundless blue homeland, countries around the world have stepped forward and taken a series of firm, effective, and feasible measures, from the rational development and utilization of resources to the careful restoration of ecosystems, from the improvement of sound institutional guarantees to extensive and in-depth public participation, to comprehensively and multi-level strengthen marine protection and strive to achieve sustainable development of the ocean.
Norway, as the world's second-largest exporter of marine products, heavily relies on ocean resources for its economic development, with approximately two-thirds of its export revenue coming from this vast blue sector. In order to achieve the rational and orderly utilization of marine biological resources, Norway has decisively abandoned the traditional and simple "relying on the sea to eat from the sea" model and instead established a strict and refined management system. By implementing a strict quota system and strictly controlling the fishing quantity, we will resolutely crack down on overfishing and illegal fishing activities. The newly revised Marine Resources Law has set more rigorous standards for fishing methods to minimize the impact of fishing on marine ecology. At the same time, Norway actively establishes a series of marine protected areas, closely integrating fisheries management with the protection of marine biodiversity. It focuses on the protection of vulnerable ecological environments such as fish fry, endangered fish species, fish spawning areas, and coral reefs, and even prohibits underwater fishing in some areas. In addition, Norway has proactively launched multiple forward-looking and comprehensive plans to protect the marine ecological environment. For example, the development of the Green Shipping Action Plan aims to reduce the impact of maritime transportation on the marine ecological environment, with the ambitious goal of halving domestic shipping and fisheries emissions by 2030; Launch the "Marine Waste and Microplastics Prevention and Development Plan" and generously allocate 1.6 billion Norwegian kroner (1 Norwegian kroner is approximately 0.8 yuan) between 2019 and 2022 to improve the management of plastic waste and actively promote global marine waste management; And cooperate with the World Bank to establish a trust fund, increasing by 46 million Norwegian kroner, to jointly carry out cooperation projects in the fields of fisheries management, marine pollution control, and integrated ocean management.
Indonesia, the world's largest archipelagic country, boasts an astonishing wealth of coral resources, including nearly 600 species of coral, with a coral reef area of approximately 2500 square kilometers, accounting for about 10% of the world's total coral reef area. Taking the Bird's Head Peninsula, located in the coral reef triangle, as an example, the surrounding waters are extremely rich in species, with thousands of different coral fish, hundreds of corals, sharks, etc., like a magical marine organism "species factory". Coastal and marine resources, represented by coral reef ecosystems, have made significant contributions to the economic development of Indonesia. Studies have shown that by 2030, healthy coral reefs could have a positive impact on the development of Indonesia's coastal fisheries and tourism industry, contributing an additional $37 billion in revenue to the country's economy. However, it is concerning that in recent years, relevant research institutions have found that about one-third of Indonesia's coral reefs are in an unstable state, and the species of coral reef organisms have significantly decreased. Global climate change, destructive fishing, increased carbon emissions, and an increase in nutrients and sediment have all caused serious damage to coral reefs. Coral reefs, as an important pillar of marine ecosystems, are of great significance. Indonesian Minister of Marine Fisheries, Eddie, explicitly stated that coral reef systems are not only habitats for various marine organisms, but also solid foundations and good platforms for the development of industries such as tourism and aquaculture. Vigorously promoting the protection of coral reef systems will help better benefit coastal populations and have a profound and positive impact on economic growth in coastal areas. As early as 1998, the Indonesian government launched the Coral Reef Conservation and Restoration Program, which was jointly implemented by the Ministry of Marine Fisheries and the Indonesian Academy of Sciences. At the same time, multiple measures aimed at promoting the protection of marine resources have been implemented, including the establishment of marine protected areas and the recruitment of local volunteers to assist in managing fishing activities. From 2003 to 2015, the total area of marine protected areas in Indonesia doubled significantly. Last October, Indonesia launched its largest coral reef restoration plan to date. This plan is not only an important component of Indonesia's national economic recovery plan, but also reflects the innovative approach of the Indonesian government to organically combine coral reef restoration with tourism. Using various scientifically effective methods to repair damaged coral reefs, restore marine ecosystems, and develop ecotourism projects to attract tourists. This plan is expected to attract over 11000 people from various industries to actively participate, creating rare opportunities for education, scientific research, and economic development in the coastal areas of Indonesia. International organizations have also played a unique and crucial role in protecting coral reefs. For many years, the World Bank has actively assisted the Indonesian government in carrying out coral reef conservation work through various means such as providing financial support and technical assistance. Under the strong promotion of the World Bank, local fishermen have received professional training in monitoring coral reef ecosystems, and some schools have also incorporated ecosystem protection into their curriculum, significantly enhancing the public's willingness and initiative to protect coral reefs. With the concerted efforts of all parties, Indonesia's coral reef protection work continues to make new progress. According to local media reports in Indonesia, coral reef ecosystems are showing new vitality and energy. Local divers observed that the damaged coral reefs have been effectively restored to a certain extent, and the number of fish has also increased. By further improving national and local coral reef protection measures, Indonesia will continuously enhance its blue economy potential and more effectively protect marine ecosystems, contributing to the global marine conservation cause.
Easter Island in Chile, located in the central South Pacific, is over 3000 kilometers away from mainland Chile and is known locally as Rapanui Island. Here stands not only a highly iconic giant stone statue, but also a treasure trove of abundant marine resources. The surrounding waters of the island are home to over 140 unique marine organisms, with a large amount of coral covering the seabed. Underwater ridges also provide important spawning grounds for economic fish such as tuna and marlin. In 2018, the Rapanui Marine Reserve was established, with a sea area of 740000 square kilometers, becoming one of the largest marine protected areas in the world. Industrial fishing and mining are strictly prohibited within the protected area, and only the traditional fishing methods of the local people are retained, cleverly integrating marine protection with the inheritance of customs and culture. During the establishment of the protected area, the islanders of Rapanui Island played a crucial role. They actively support the establishment of protected areas and have jointly negotiated with the government to establish a scientific and reasonable supervision and protection plan. Some islanders have also received professional training and become responsible supervisors of protected areas. This protection model that fully mobilizes the enthusiasm of the public has gained high recognition and heartfelt support from the local people. Chile has a coastline stretching over 6400 kilometers, and in recent years, the scope of Chile's marine protected areas has rapidly expanded, reaching 43% of its exclusive economic zone area. At present, Chile has four types of marine protected areas, including marine parks, marine conservation areas, nature reserves, multi-purpose marine and coastal protected areas. Among them, marine conservation areas focus on protecting key areas such as breeding grounds for marine organisms and fish gathering areas, while multi-purpose marine and coastal conservation areas allow for sustainable economic activities with minimal environmental impact, such as manual fishing and ecotourism, while implementing marine protection measures. The establishment of the protected area fully demonstrates the Chilean government's firm determination to protect the ocean. Chilean ecological expert Miriam Fernandez emphasized that Chile not only needs to effectively transform the planned protected areas into truly effective protected areas, but also should further increase efforts to protect ecologically fragile areas that are greatly affected by coastal fishing activities. Overfishing and illegal fishing, as well as improper use of chemicals in aquaculture, have seriously endangered marine ecology and have become key areas of focus for the Chilean government to address. In 2020, the Chilean Fisheries and Aquaculture Administration, in collaboration with 10 institutions including the military, customs, taxation, health, and environmental supervision, officially established the "Sustainable Fisheries and Aquaculture Review Network" to strengthen strict supervision and management of the entire value chain, including fishing, landing, transportation, and marketing. In addition, the Chilean government also requires fishing boats to install cameras to record the entire fishing process from departure to landing. The survival status of marine organisms has also received close attention and high attention from the Chilean government. Taking whales as an example, ship collision is one of the important factors threatening the survival of whales. In order to better protect whales, Chile recently launched a pilot conservation project and installed intelligent buoys capable of detecting whale positions in the Corcovado Bay, where blue whales gather. Once a whale appears, the buoy will quickly issue a satellite alert, and the onshore center will promptly remind nearby ships to take preventive measures upon receiving the alert, effectively avoiding collision accidents. In addition, the intelligent buoy is equipped with sensing devices for monitoring temperature, pH value, nutrients, and oxygen. The data collected can be used by researchers to track the health status of the ocean, providing valuable information for monitoring the global warming process. Marine organisms are able to absorb heat and sequester carbon dioxide, making them important ocean carbon sinks, "said Carolina Schmitt, Chile's Minister of Environment." Strengthening the protection and sustainable management of the ocean is crucial for maintaining marine biodiversity and unique ecosystems, and can better play the key role of the ocean in addressing climate change
South Africa, a country surrounded by the sea on three sides and with a coastline of about 3000 kilometers, receives a large amount of plastic waste into its surrounding waters every year. In order to address this severe challenge, South Africa has strengthened strict control over marine plastic pollution in various legislation such as the National Environmental Management Act, the Waste Act, and the Agriculture Act. It has vigorously promoted the implementation of key measures such as estuarine management plans and the establishment of marine protected areas, making every effort to enhance marine environmental protection. On the lagoon beaches of Cape Town, one can often see a four wheeled cart carrying two large blue barrels, with a roaring motor. Local volunteers hold yellow suction tubes and carefully clean up cigarette butts, straws, and other garbage on the beach. This large 'vacuum cleaner' plays an important role in cleaning and screening plastic waste on the beach. As is well known, plastic is generally not biodegradable and will only become smaller and smaller. If plastic waste on the beach is not cleaned up in a timely manner, it may be ingested by seabirds and other animals, or carried into the sea by waves, causing serious pollution to the marine environment. And this advanced vacuum cleaner can suck in a large amount of sand particles containing tiny plastics, and then cleverly filter out the sand, leaving only plastic waste. Professor Peter Ryan from the University of Cape Town clearly stated in a study published in May last year that approximately 60% to 90% of plastic waste from land is expected to remain on beaches, and the vast majority of it can be collected and cleaned up, effectively avoiding entering the ocean. Therefore, improving the management of solid waste and preventing garbage from entering the sea with rivers is of decisive significance for reducing plastic waste in the ocean. At present, the South African Department of Environment, Forestry and Fisheries is actively promoting a new project funded by the Global Environment Facility, which plans to work together with local governments, non-profit organizations, and businesses to comprehensively clean up and recycle garbage in five river systems located in the KwaZulu Natal province in eastern South Africa. This project will implement innovative measures such as increasing garbage cleaning and collection, developing community led garbage classification, and waste recycling to carry out source control and resolutely prevent garbage from entering the ocean. At the same time, South Africa is also tirelessly seeking alternatives to plastic. The report "Exploring the Potential of Using Alternative Materials to Reduce Marine Plastic Waste" released by the United Nations Environment Programme states that "removing all plastic from society is neither realistic nor desirable, but finding alternatives to reduce our dependence on plastic can play a crucial role. Recently, a biotechnology company based in Johannesburg, South Africa, successfully released a "bioplastic" that it had carefully developed over two years. This product is developed by extracting wood chips into lignin and utilizing advanced nanotechnology. According to the company's leader Mangole, this "bioplastic" has the unique advantage of dissolving in water within 36-72 hours and completing the biodegradation process in water. This product has been successfully nominated for the "2021 African Engineering Innovation Award". In the initial stage, 'bioplastics' will mainly be used to replace disposable plastics in the food packaging industry, including straws, tableware, and films needed for packaging fruits and vegetables, and will gradually be promoted to other fields such as the pharmaceutical industry, "said Mangole. In order to raise people's awareness of ocean conservation, South Africa has designated the second week of October each year as National Ocean Week. During Ocean Week, many schools and environmental organizations actively carry out beach walks, where participants carefully collect garbage on the beach while educating the public on ocean protection. In the 2020 Ocean Week event, the South African Wildlife and Environment Association, in collaboration with the South African Department of Science and Innovation and other organizations, held an online seminar on important topics such as "How to reduce marine plastic waste pollution". Participants from all over South Africa were organized for in-depth online discussions and learning. According to the environmental magazine "Down To Earth", Africa is one of the regions with the highest population growth rates in the world. With rapid economic growth, the consumer market for plastic products is further expanding, and a large amount of plastic waste is generated, which has a very adverse impact on the survival of marine life. Therefore, more countries and social forces need to work together to jointly control marine garbage pollution and fully protect the marine ecological environment.
Marine conservation is an urgent global task, and the active actions and unremitting efforts of countries around the world have laid a solid foundation for safeguarding the blue sea and sky and building a blue future. We believe that with the continuous collaboration and persistent efforts of all countries, the vast and boundless ocean will always benefit humanity. We look forward to a better blue future together!
 Lighting up the Light of Memory for Alzheimer'
Lighting up the Light of Memory for Alzheimer'
 The Netherlands launches pilot vaccination for avia
The Netherlands launches pilot vaccination for avia
 Simon Fisher Becker, who played the "Fat Monk"
Simon Fisher Becker, who played the "Fat Monk"
 Direct talks with Hamas have angered Israel, with U
Direct talks with Hamas have angered Israel, with U
 Elon Musk: If Starlink is shut down, the entire fro
Elon Musk: If Starlink is shut down, the entire fro
 Syrian transitional president calls for maintaining
Syrian transitional president calls for maintaining
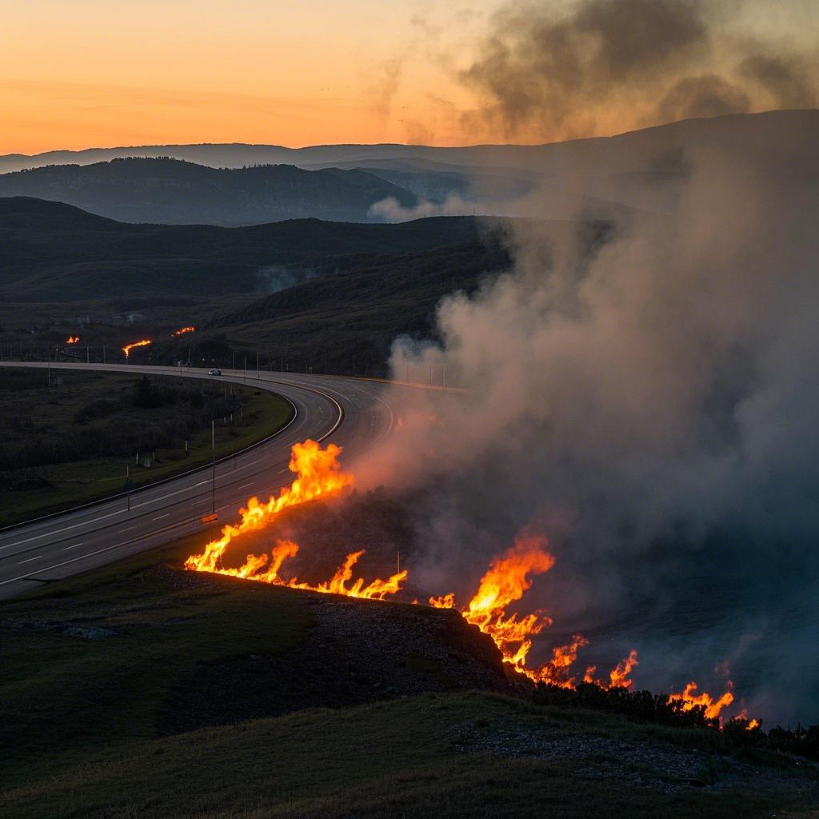 The West Hampton Wildfire in Long Island, USA has b
The West Hampton Wildfire in Long Island, USA has b
 New regulations in the UK create waves: fines for t
New regulations in the UK create waves: fines for t
 The UK High Court&#039;s ruling that child
The UK High Court&#039;s ruling that child